Python Database API Specification for Oracle Database – II
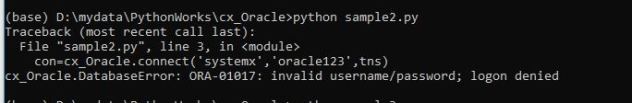
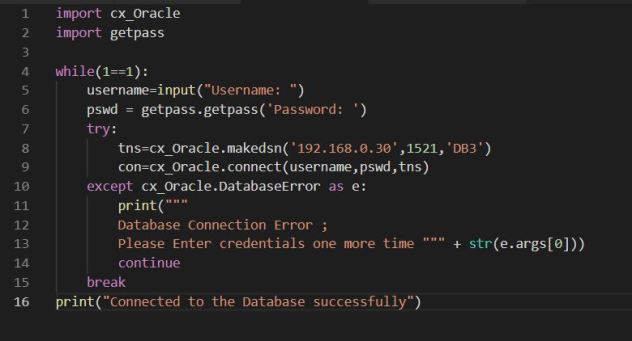
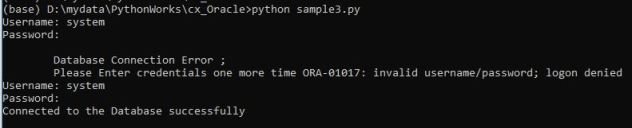
This is my third note about about Python Database API Specification for Oracle Database. In my last note; I showed how you can connect to Oracle database in detail.
In this note; I will show you how you can execute SELECT statement and fetch data from Oracle database in Python.
In order to execute an SQL statement in Python; you need to create a cursor object from a database connection. After creating a cursor ; you can execute many statements; These statements can ben DDL or DML. All statements are executed with execute() function. Simply at least one time you should call execute() function. But for the SELECT statement you have to call fetch statements once or many time after execute() function.
Now Let’s look at cursor functions.
cx_Oracle.Cursor.parse() this is an optional function to check the correctness of the SQL statement.
cx_Oracle.Cursor.execute() : This function can be used for to execute a SQL statement
If you are executing a SELECT statement; you should call fetch functions additionally which are given below
cx_Oracle.Cursor.fetchall() : This function can be used for fetching all records from the SQL query
cx_Oracle.Cursor.fetchmany() : This function fetches the next rows_no rows from the database
cx_Oracle.Cursor.fetchone(): This function fetches a single tuple from the database.
Now I will explain how you can execute SELECT statement and fetch query results in Python.
First; you need to create a cursor object with cursor() function from a database connection like below.
import cx_Oracle
db_con=cx_Oracle.connect(‘scott/oracle@192.168.56.100:1521/DB3’)
cur=db_con.cursor()
After creating your cursor object; you can run the SELECT statement and fetch the query result. The query results are put into the list object. The cursor that you created simply points this list object; and the all data can be fetched with a simple loop like the below sample
import cx_Oracle
db_con=cx_Oracle.connect(‘scott/oracle@192.168.56.100:1521/DB3’)
cur=db_con.cursor()
query=’Select * from emp’
cur.execute(query)
for x in cur:
print(x)
cur.close()
Now run this sample and look at the result.
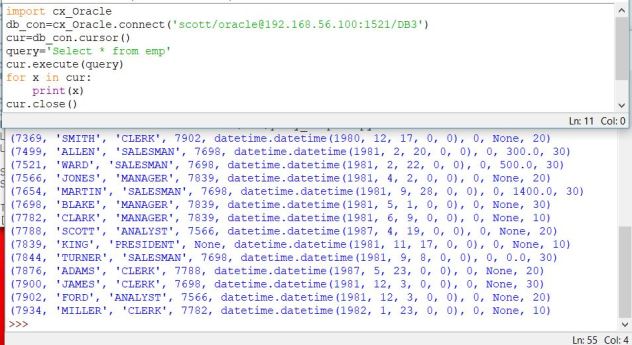
As you see; printing query result with the print statement is not a good option. Therefore ; I will advice you to use tabulate module to format the query result easily.
you can install the tabulate module with the below command.
pip install tabulate

At the below example you will see the usage of fetchall() function and tabulate module. Tabulate module can be called from the print function.
from tabulate import tabulate
import cx_Oracle
db_con=cx_Oracle.connect(‘scott/oracle@192.168.56.100:1521/DB3’)
cur=db_con.cursor()
query=’Select * from emp’
ret=cur.execute(query)
result=cur.fetchall()
header=[‘EMPNO’,’ENAME’,’JOB’,’MGR’,’HIREDATE’,’SAL’,’COMM’,’DEPT’]
print(tabulate(result,header,tablefmt=”grid”))
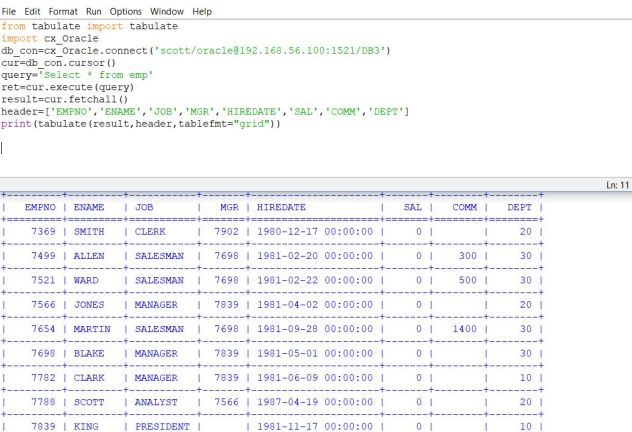
Another example is the use of fetchone() function. By this function you can fetch the query result one by one.
import cx_Oracle
db_con=cx_Oracle.connect(‘scott/oracle@192.168.56.100:1521/DB3′)
cur=db_con.cursor()
query=’Select * from emp’
cur.execute(query)
row=cur.fetchone()
print(row)
row=cur.fetchone()
print(row)

In the next notes; I will show you how you can use bind variables in SQL statements. I hope that this note will be helpful for you to understand the SQL statement usage in Python.
Anıl Akduygu
Istanbul
SRKN 19:39 on 23 April 2019 Permalink |
Hi Anıl,
You’re the best DBSEC pro that I’ve seen ever.
Thank you for good shares.
Regards
LikeLike